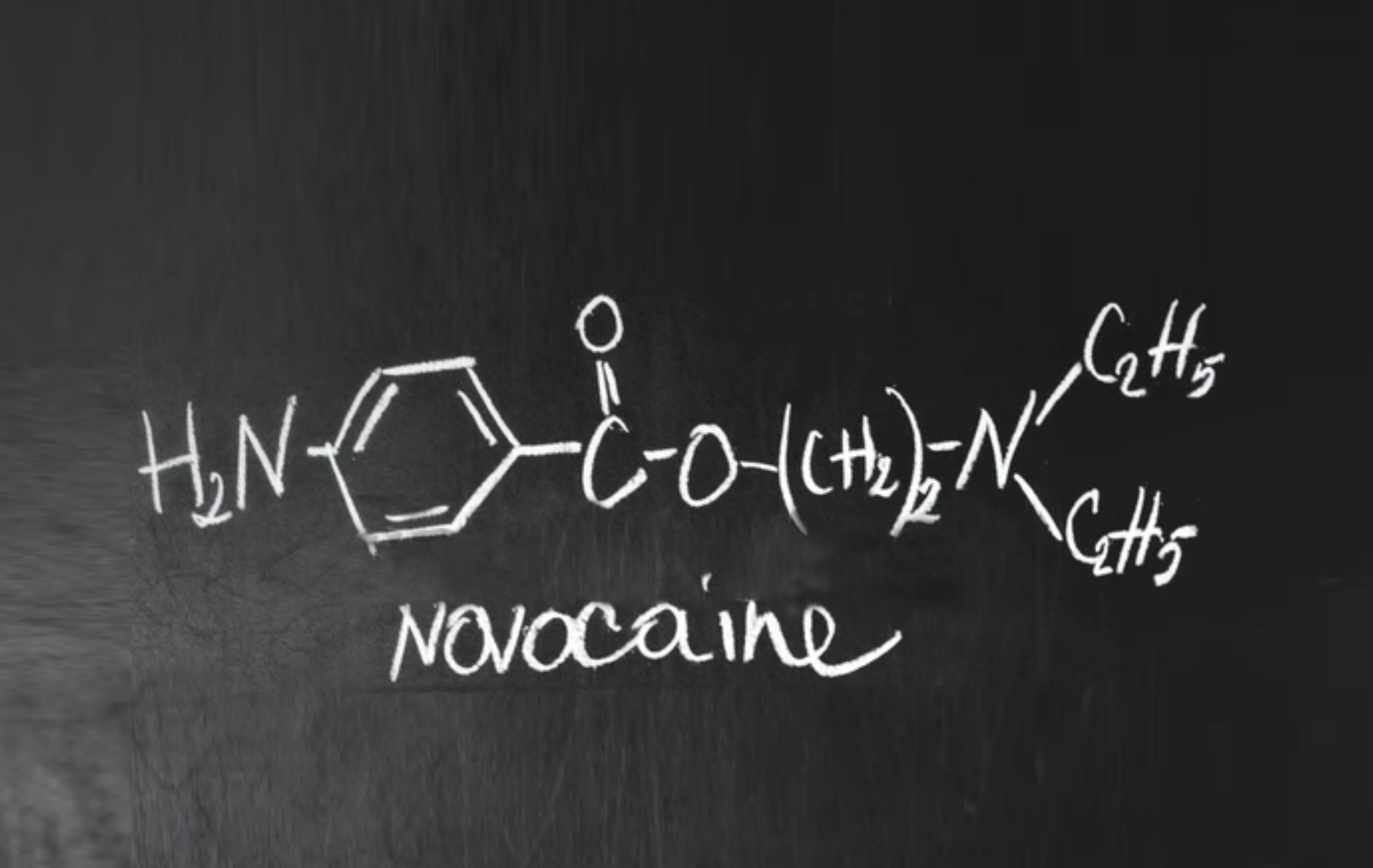
Chlorohydrate of Procaine procaine is used as an anaesthetic during surgery and dental procedures to inhibit the sensation of pain, with less discomfort than lidocaine. Patients may receive the anaesthetic during minor surgery or dental procedures to cause a lack of sensitivity in areas of the skin and mucous membranes. It acts mainly by blocking sodium channels so that they do not reach nerve cells.
Want to find out more about Procaine: Keep reading the article below!
What is procaine?
In the past, procaine was part of the composition of pharmaceutical formulations suitable for both parenteral and topical application. However, as of today, commercially available procaine-based medicines are only for topical use (skin cream, ear drops, dental solution, and dental drops). These medicines are classified as over-the-counter (OTC), so, it is allowed the free sale in procaina cloridratopharmacies and parapharmacies.
In drugs containing procaine, procaine is normally present in the form of procaine hydrochloride and in some products is found in association with other active ingredients, such as phenazone (with anti-inflammatory action), benzocaine (also with anesthetic action) and 8-oxyquinoline sulfate (with antiseptic properties).
Procaine action to reduce pain sensitivity
Procaine is a local anaesthetic. It acts primarily by inhibiting the entry of sodium into peripheral nerve cells, thereby blocking the transmission of nerve impulses and causing loss of sensation in the skin and mucous membranes.
It’s’ metabolized in the plasma by the enzyme pseudocholinesterase through hydrolysis into para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), which is then excreted by the kidneys into the urine. Like the other active ingredients with this kind of properties, procaine is able to accomplish its action by interacting with the voltage-dependent sodium channels present on the neuronal cell membrane of peripheral nerves. Through this interaction, procaine inhibits the permeability of the cell membrane to sodium, blocking its entry into the nerve cell. As a result, nerve cell excitation and transmission of the pain stimulus is prevented. in addition, this agent increases electrical excitation threshold, reduces rate of rise of action potential and slows nerve impulse propagation thereby causing loss of sensation. The receptor site is thought to be located at the cytoplasmic (inner) portion of the sodium channel. Procaine has also been shown to bind or antagonize the function of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors as well as nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and the serotonin receptor-ion channel complex.
How is procaine used to be taken?
The use of procaine should only be done for short periods of time. In the pharmaceutical formulas in which it appears, is indicated for:
- the treatment of mouth or dental pain, from caries, periodontitis and pulp disease. It is prescribed by means of dental solution in spray bottle or odontalgic drops;
- the treatment of pain in ear affections (e.g. otitis) without tympanic perforation. It is prescribed by ear drops;
- the treatment of pain and symptoms caused by superficial wounds, excoriations, insect bites, minor burns, sunburn and skin irritations caused by chemical or physical agents. It is applied by cutaneous cream.
Procaine is present within Flarer portfolio of pharmaceutical raw materials. The quality of our active pharmaceutical ingredients is constantly monitored by the validation of our suppliers around the world, through audits (documentary and on-site), a thorough scouting process and the commissioning of raw material analysis and verification.Regularly inspected by Swissmedic, Flarer has stood out for its seriousness and responsiveness, due to its lean structure that allows to act quickly in relations with suppliers and customers.
Contact our experts to find out more about Procaine and our pharmaceuticals ingredients! Click here!